Forging New Ties: The India–UK FTA and Its Role in Global Trade Evolution
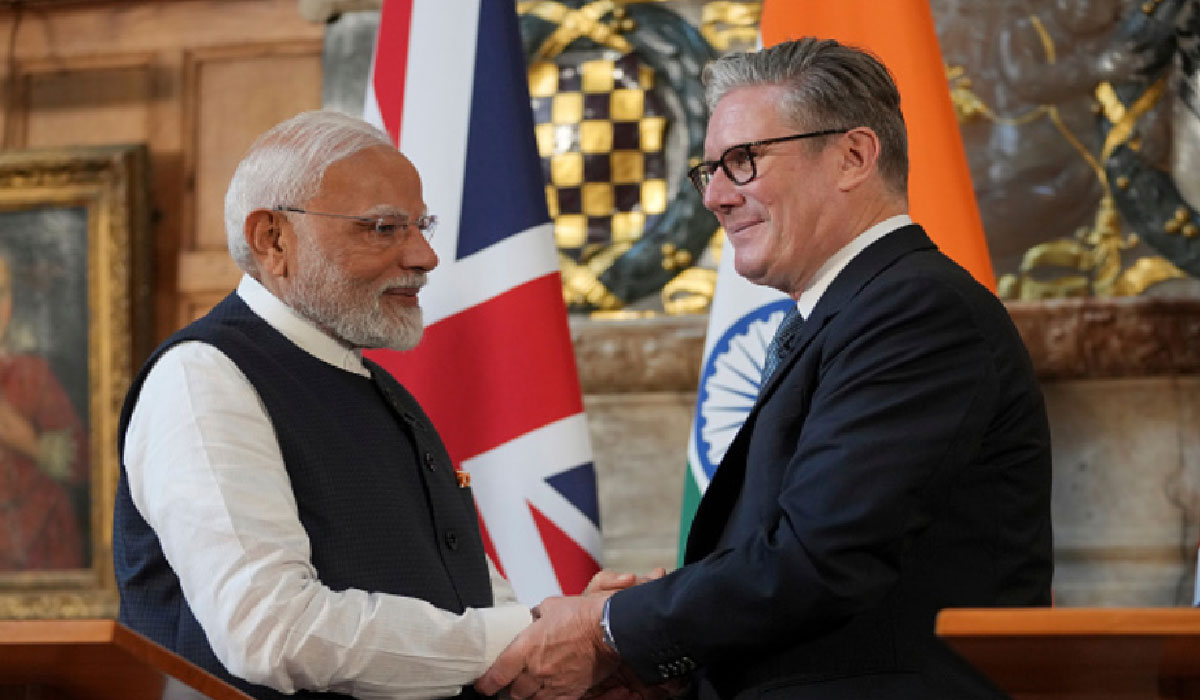
The India–UK Free Trade Agreement (FTA), signed on July 24, 2025, marks a historic milestone in the bilateral relations between two influential democracies with long-standing historical ties. This landmark deal not only deepens economic cooperation but also signals a strategic shift in global trade dynamics, as both nations adapt to the realities of a post-Brexit and increasingly multipolar world.
A New Era of Economic Partnership
The FTA represents the culmination of years of negotiations aimed at boosting trade, investment, and collaboration across sectors such as technology, pharmaceuticals, financial services, renewable energy, and agriculture. By removing tariffs on nearly 95% of traded goods and easing regulatory barriers, the agreement is expected to significantly increase bilateral trade volumes—projected to exceed $100 billion by 2030.
For India, the deal opens enhanced access to the UK’s service-driven economy, providing opportunities for Indian IT, pharma, textiles, and skilled labor sectors. In return, UK businesses gain greater entry into India’s vast and growing consumer market, particularly in areas such as premium goods, financial services, and education.
Strategic Alignment in a Changing World
Beyond the economic benefits, the India–UK FTA underscores a deeper strategic alignment. Both countries view the agreement as a framework for broader geopolitical cooperation—particularly in the Indo-Pacific region, where India is a key player and the UK seeks a stronger post-Brexit footprint.
The agreement also reflects a mutual commitment to high standards in sustainability, labor rights, and digital trade. Notably, it includes provisions on green technology cooperation, climate financing, and intellectual property protection, aligning economic goals with shared values.
Global Trade Implications
The India–UK FTA challenges the traditional dominance of large multilateral trade agreements by showcasing the power of well-structured bilateral deals. It sends a clear signal that strategic partnerships between emerging and established economies can yield significant mutual gains—setting a precedent for future trade alignments.
As India continues to position itself as a global economic powerhouse and the UK redefines its global role post-Brexit, this agreement may serve as a blueprint for similar deals with other major economies. For global trade observers, it represents a recalibration of economic alliances that reflects both changing political realities and evolving commercial priorities.
Key Highlights of the India–UK FTA for International Business
- Elimination of Tariffs on Majority of Goods
Over 95% of tariff lines have been reduced or eliminated, particularly in textiles, automotive parts, electronics, and agriculture. This reduces costs and increases competitiveness for exporters and importers on both sides. - Greater Access to Services Market
The FTA significantly liberalizes services sectors including financial services, legal, accounting, insurance, healthcare, and IT. This opens new avenues for cross-border service providers and investors, especially in fintech and consultancy. - Eased Mobility for Skilled Professionals
A streamlined visa and mobility framework facilitates easier movement for professionals, entrepreneurs, and students, which is crucial for multinational firms and joint ventures reliant on cross-border talent and knowledge exchange. - Investment Protection & Dispute Resolution Mechanism
Clear provisions on investment protection, intellectual property rights (IPR), and an independent dispute resolution mechanism reduce risk for foreign investors and encourage long-term capital flow. - Digital Trade & E-Commerce Facilitation
Provisions on data flow, cybersecurity, digital payments, and e-commerce regulation provide clarity and predictability for digital businesses operating across borders, including tech startups and large multinationals. - Sustainability & Green Economy Provisions
The agreement includes commitments to promote green technologies, carbon-neutral investments, and climate-resilient infrastructure—creating new opportunities in renewables, ESG financing, and sustainable supply chains. - Customs Cooperation & Trade Facilitation
Simplified customs procedures, harmonized standards, and mutual recognition of conformity assessments will accelerate logistics, reduce administrative costs, and enhance supply chain efficiency. - Opportunities for Third-Party Collaboration
The FTA enables companies based in India or the UK to leverage the deal as a gateway into other regions (e.g., EU via the UK, or ASEAN/Africa via India), encouraging hub-and-spoke models for international trade.
Looking Ahead
The real success of the India–UK FTA will depend on effective implementation, ongoing dialogue, and mutual responsiveness to future challenges. But what’s already clear is that the agreement goes far beyond tariff reductions—it reaffirms the potential of economic diplomacy to reshape international relationships and foster inclusive growth.
In forging new ties, India and the UK have not only strengthened their own partnership—they have helped redraw the map of global trade.